Home blood pressure monitoring
Learn how to use Withings home blood pressure monitoring devices to track and manage high blood pressure efficiently. Get reliable insights...
One-third of adults have high blood pressure, also known as hypertension—and many don’t know it. This dangerous condition can do lasting damage to your health if it remains untreated. Discover the symptoms and effects of hypertension, and see how regularly monitoring it can help detect high blood pressure before the onset of complications, and help you control it.

Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers.
The first is the systole, when the heart contracts and ejects blood into the arteries.
The second is the diastole, when the heart relaxes. The reading is a unit of pressure expressed as millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
It is generally written as "120/80 mm Hg."
Blood pressure has a daily pattern. During the day, your blood pressure continues to rise. It usually experiences a peak in the middle of the afternoon. In the evening, BP begins to decrease. Normally, it should be lower at night, when you are asleep.
"Blood pressure can be highly variable. Thus the diagnosis of hypertension should not be based on a single set of blood pressure readings at a single office visit, unless the blood pressure is substantially increased."
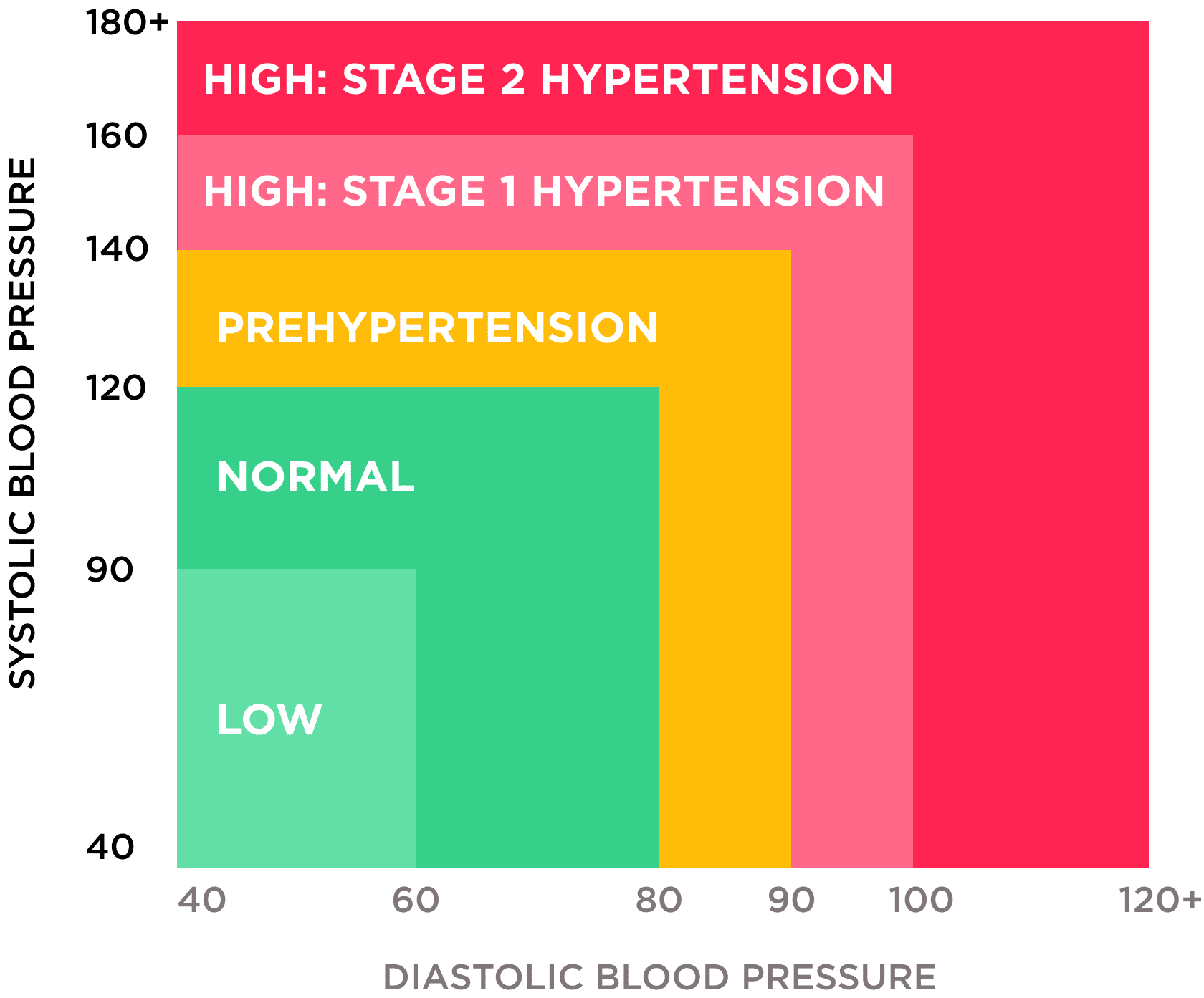
According to the European Society of Cardiology, systolic pressure of less than 120 and diastolic pressure of less than 80 is a normal, healthy blood pressure.
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is above 140/90 mm Hg for an adult.
When a person suffers from hypertension, it means that the walls of their circulatory system are constantly under too much strain.
Some strong evidence shows that high blood pressure is more common among people who have the following risk factors:
Family history
If your parents or other close blood relatives have high blood pressure, there’s an increased chance that you’ll suffer from it.
Gender
Until age 64, men are more likely to get high blood pressure than women are. At 65 and older, women are more likely to get high blood pressure.
Advanced age
The older you are, the more likely you are to get high blood pressure.
Drinking too much alcohol
Heavy drinkers are also more likely to develop hypertension.
An unhealthy diet
Consuming too much salt and saturated fats may increase blood pressure levels.
Overweight
There is a strong link between obesity and hypertension, and weight reduction has been shown to lower blood pressure.
Chronic kidney disease
High blood pressure may occur as a result of kidney disease.
Hypertension is often underdiagnosed because it may not show symptoms. High blood pressure warning signs may include:
• Chest pain
• A constant or severe headache
• Difficulty breathing
• Irregular heartbeat
• Blurred vision
• Palpitations
• Sweating
• Dizziness
• Nausea
• Nosebleeds
When your blood pressure becomes very high—above 180/110 mm Hg—you might experience an hypertensive crisis. There are 2 types of high blood pressure crisis:
Hypertensive urgency: a severe uncontrolled hypertension uplift that does not show evidence of organ damage.
Hypertensive emergency: the blood pressure elevation is so high that it causes organ damage (brain, eyes, heart, etc.)
Hypertensive crisis isn't something that happens often, but when it does, it's a serious situation requiring immediate medical attention. It's a stark reminder of just how crucial it is to manage chronic high blood pressure. Think regular blood pressure checks, taking your medication as prescribed, and being upfront with your healthcare provider about any health concerns or changes. If you're living with high blood pressure, understanding your condition and partnering with your doctor to keep your blood pressure in a healthy range is your best defense against complications like this.
Hypertension is the most common chronic disease in the world and is considered a major cardiovascular risk factor.
As it can be difficult to alert people to an increase in their blood pressure, hypertension is often called “the silent killer,” as it can damage you heart in various ways.
Hypertension increases the risk of developing heart failure, a dangerous condition in which the heart cannot pump enough blood throughout the body.
People who have high blood pressure are at a higher risk for atrial fibrillation (AFib), an anomaly of the heart’s electrical activity, which is often asymptomatic. AFib may lead to stroke, heart failure and cognitive decline. Learn more about AFib +
Also called ischemic heart disease, this is a frequent complication in hypertensive patients. Under too much strain, the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart can become too narrow, reducing blood flow in the heart.
Common in people who have uncontrolled high blood pressure, this condition thickens the walls of your heart's main pumping chamber. The result is an enlarged heart that can lose the ability to pump with proper force.
This condition, in which one or more of your four heart valves doesn't work properly, is thought to be linked with elevated blood pressure. Learn more about VHD +
Because high blood pressure is often "silent," with no symptoms, many people may have hypertension without knowing it. Monitoring your blood pressure at home may enable you and your physician to detect hypertension before the onset of complications.
Home monitoring is recommended for all people with high blood pressure for better control, and to help the healthcare provider to determine whether treatments are working.

Home blood pressure monitoring
Learn how to use Withings home blood pressure monitoring devices to track and manage high blood pressure efficiently. Get reliable insights...

How Do You Know You Have Sleep Apnea
Learn how Withings sleep tracking can help indicate if you have sleep apnea. Discover the signs of obstructive sleep apnea and how a sleep...

Hypothyroidism and weight: How thyroid issues affect weight gain
Learn how hypothyroidism affects weight gain, appetite loss, and metabolism. Understand the thyroid's role and tips to manage weight...

What is BMI? Understanding Normal Body Mass Index for Men and Women
What is BMI? Body Mass Index helps determine if you're underweight, normal weight, or overweight. Learn how BMI works for men and women.
on your first order by registering
By registering, you agree to receive advertising e-mails from Withings. However, if you change your mind, you can unsubscribe at any time. *The discount is valid for any purchase (except BeamO and U-Scan Nutrio) of at least €100 for 30 days after reception of the code. Only valid on withings.com, and while supplies last. This offer is only valid for first-time purchases. These offers cannot be combined.

